When you are just getting started in photography, there are days you will take flat and seemingly lifeless photos. But that happens even to experienced photographers who forget a thing or two about photography and, therefore, end up missing a shot.
While photography may look simple and straightforward, seeing that we can all do it on our mobile devices, there are different aspects to put into consideration to capture professional quality photos. Focus and exposure are two of such factors. You need to ensure that you get the lighting right, balance the elements of your photo and much more.
Your camera sets most of the aspects automatically, but sometimes, you will need to tweak the settings to get a good photo based on the shooting situation. Granted, you will need to know your camera in and out.
Know Your Camera
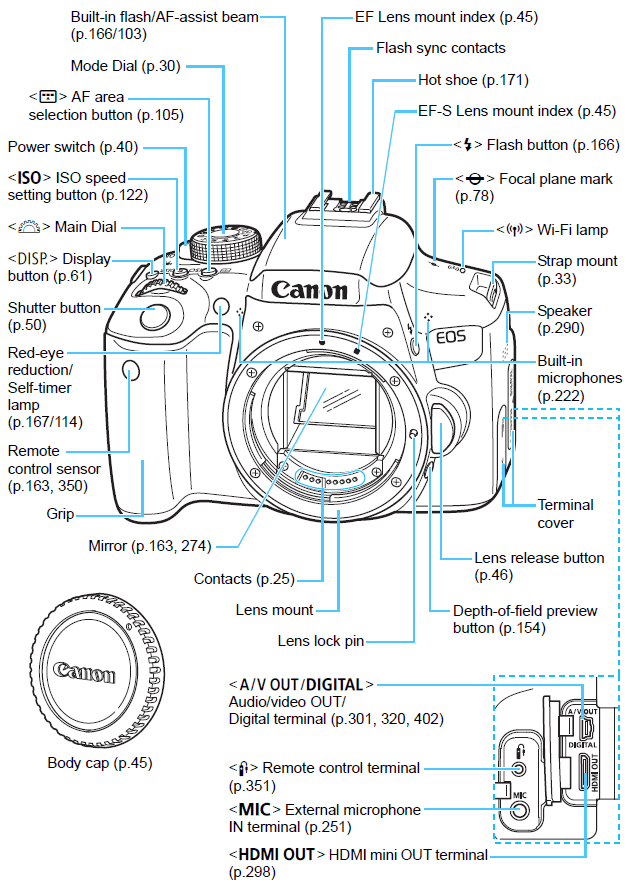
Cameras are offered differently; they vary in size, shape, aperture and features. However, there are buttons and features that you will find in almost all cameras. Some of the common parts include:
Shutter Button
This is the button you push to capture a photo. Most of the digital cameras in the market today have a 2-stage shutter button. This allows you to push it halfway down or all the way down. When pushed halfway, the button locks in the focus or photo exposure, and when pushed all the way down, the shutter button takes a photo.
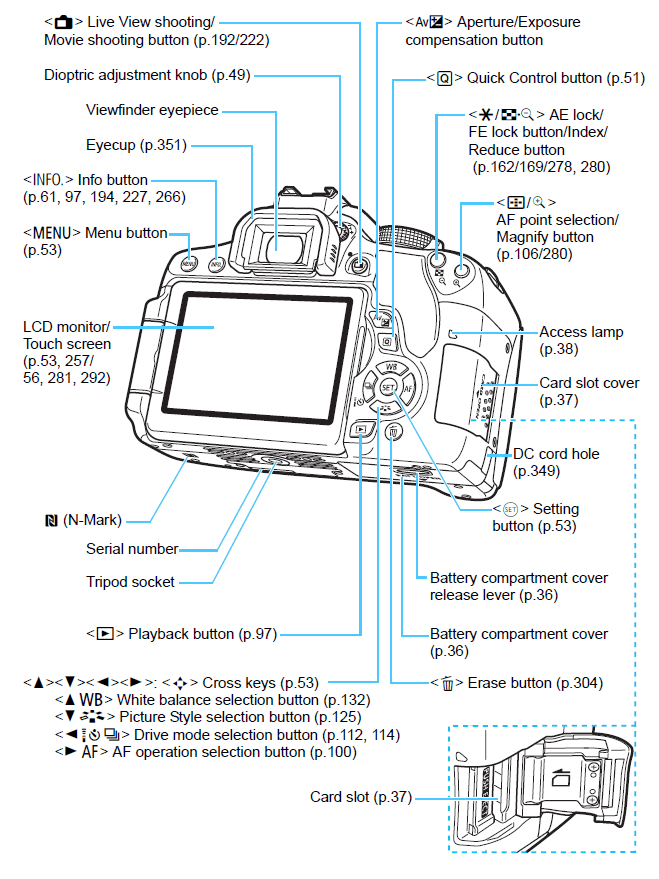
LCD Screen
The LCD screen on your digital camera allows you to frame a shot, view photos you have taken, and change the settings of your camera with ease. When used right, the LCD will allow you to control lighting, white balance and the balance between photo components. Again, you control how much you zoom in or out.
(Canon)
(Canon)
Menu And Mode Buttons
The Menu and Mode buttons allow you to tweak the settings of your camera to meet your shooting situation. Some cameras will have both the buttons while some will have just one. Some of the settings you can change include shutter speed, activate or deactivate photo flash, contrast and brightness, change scene mode to video mode and much more.
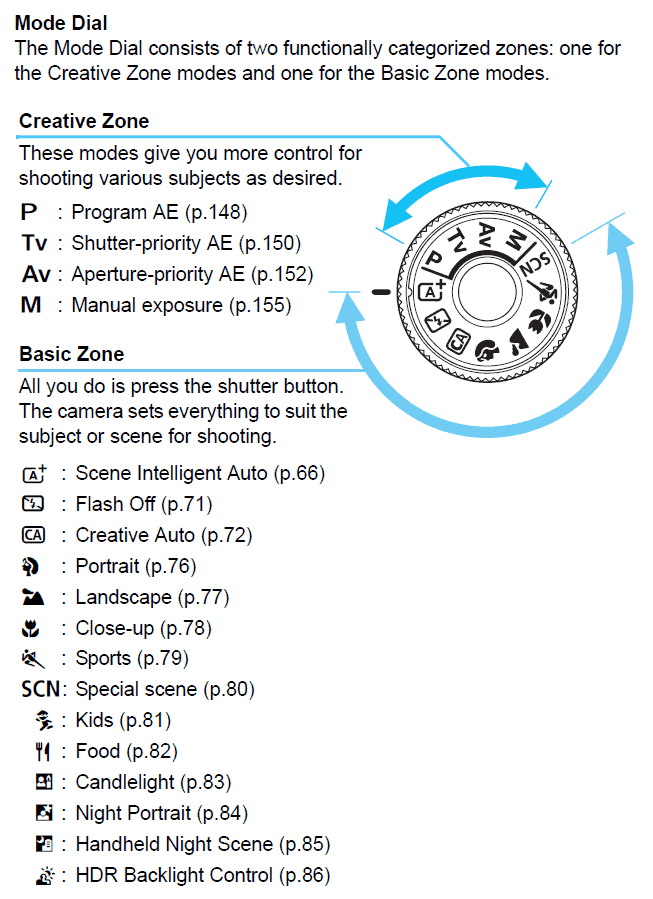
SLR cameras are now offered with a mode dial, which you rotate to change the settings of your camera. From the dial, you can select portrait, landscape, special scene, sports, manual, shutter priority, aperture priority and much more. The dial lets you change settings with ease.
Zoom Buttons Or Ring
The zoom buttons let you zoom in or out. They will be labeled W, for wide, or T, for tight. In advanced SLR cameras, zooming is done from the wheel that encases the lens. Here, you rotate the wheel left or right to zoom in or out. In other camera’s, there is a dial around the shutter from where you zoom.
Play Button
This is button you push on when you want to view the photos or videos you have taken. While viewing the photos, you can use the zoom buttons to see more details on the photos. This will allow you to determine whether a photo was on focus and whether it has good framing.
This button is used together with the scroll wheel, which allows you to scroll through photos or navigate through the menu of your camera.
Trash Button
This is the button you push when you want to delete a photo.
Input/Output Terminals
On the sides of the camera are input and output terminals that allow you to connect your camera to accessories. One side has a memory card port. Next to the port is a door release light that shows you whenever the card door is open.
On the other side of the camera are A/V, USB and HDMI access ports from where you can connect your camera to a computer or a larger screen for photo viewing or photo editing. On the same side is a microphone jack, which you can use when recording or taking videos and a remote control terminal for better control of your camera.
On top of these ports is a speaker grill, indicating the position of your camera’s speaker. However, the speaker can be located in different parts of a camera.
The Frontal Part Of Your Camera
The lens is the main part on the front side of your camera. When the power button is pressed, the lens extends out and retracts when the camera is switched off. Most SLR cameras, however, have a lens release button from which you release the cap that keeps your lens protected.
On the lens casing is a focus ring and a zoom ring. The focus ring lets you attain a clear image. On the frontal part is a focus and an image stabilization switch, which you use to stabilize the image before capture.
When shooting at night, you can use the built-in flash at the top of your camera to light up the scene or object to be captured.
Understanding Your Camera To Get Much Better Photos
Exposure
Digital cameras are offered with a sensor behind the lens. The sensor acts like the roll of film in traditional cameras; it is the part that will actually capture a photo. However, the sensor is never taken out of the camera. When you are taking a photo, the sensor will be exposed to light for a very short period. The amount of light captured when the sensor is exposed to light is called exposure. Some cameras allow the sensor to be exposed for a period longer than a fraction of a second.
When the exposure is not right, your photos will be too bright or too dark. In most cases, your camera will adjust the exposure automatically. In other times, you will have to manually adjust the exposure of your camera to get good photos.
Focus
When the subject of your photo is in focus, they will have no blur and will appear sharp. In some cameras, focus is handled automatically and all you need to do is hold the camera stable. However, when that happens, your camera might try to focus on another object, which might cause your subject to go out of focus.
On the LCD screen of your camera, a focus indicator will be shown. This is a box that shows you what the camera is focusing on. Whenever you are taking a photo, keep an eye on the focus indicator. On most DSLR cameras, however, there is a focus ring that you use to tweak the focus of your camera and an image stabilization button that helps you reduce blur.
There is a viewfinder, which occurs as a window above the LCD screen, which shows you the auto-focus information. For a good focus, however, stick to manual focusing.
Common Camera Settings
Most cameras are designed to work automatically. This allows them to adjust to different shooting situations. However, there are settings you will like to change for better quality photos. On top of each button on your camera, there is an icon indicating what the button does. These icons are universal and appear on each camera. For instance, the bin icon indicates trash/delete/erase.
Flash: In low-light conditions, you can activate the built-in flash of the camera. However, the flash is, in most cases, automatically activated.
Timer: This comes in handy when you are taking a group photo. You can set the timer, which allows you to join the group. The camera is placed on a table or tripod for stability.
Macro Mode: This is a setting that allows your camera to capture closeup shots. With this setting, your camera can take photos just a few inches away.
Exposure Compensation: If your photos are coming out too dark or too bright, you can use this setting to control exposure; either increase or reduce exposure.
For other settings, refer to the Know Your Camera section above.
Shutter Speed, ISO And Aperture
Getting the right exposure is key in getting a good quality photo. When you are controlling the exposure of your camera, you only need to tweak three settings; aperture, shutter speed and ISO. When set right, these settings allow you to take photos in different situations and lighting conditions from bright sunny days to low-light conditions.
Like a horde of other settings, your camera will automatically control these three settings. However, you can actually control these three settings by selecting different modes on your camera and by adjusting the amount of light that goes through the lens of your camera. DSLR camera allows more manual control over the camera’s exposure, which explains why they are a favorite of many professional photographers.
Shutter Speed
Shutter speed is the amount of time that the camera’s shutter stays open. When a camera has a slow shutter speed, for instance 1/4 second, the camera gathers more light for clear images. When your camera has a fast shutter speed, for instance 1/2000 second, it freezes the action, thereby, avoiding blurry photos. The latter is ideal when you are capturing moving objects such as in sports.
When using a tripod and capturing stationary objects, a slow shutter speed will give you clear and sharp photos. When used right, both the slow and the fast shutter speeds will give you great photos.
Aperture
The lens of your camera has a circular opening that controls the amount of light that reach the sensor. This works the same way as the pupil of our eyes. The size of this opening is referred to as aperture, f-stop or f-number. The aperture and the shutter speed control how much light gets to the sensor of your camera.
When your camera has a wide aperture such as f/1.4, a faster shutter speed will be needed to get clear sharp photos. With a narrow aperture, for instance f/16, a slower shutter speed will be needed for sharp images.
The aperture also regulates the way light is focused on your camera. With a wide aperture, you will have a blurry background, but the photo subject will stay in focus. When this happens, the effect is known as a shallow depth of field.
ISO
When using a digital camera, you can control the sensitivity of the sensor. Sensitivity is shown in form of ISO number. When the sensitivity of your sensor is low, for instance ISO 100, the camera will require more light to create a good exposure. This means that, in such a case, the camera will have either a wider aperture or a slower shutter speed in order to gather more light.
Cameras with a high ISO number, such as ISO 3200, have a very sensitive sensor, allowing them great exposure even in low light conditions. However, when the ISO number is high, there will be more photo noise and the photos might appear grainy.
For sharp photos, ISO, aperture and shutter speed should balance. While these elements are balanced automatically, you can control them when you feel the quality of the photos are not as you would want.
Depth Of Field
Focus, just like exposure, is very important in any photo you take. But, there are times you need the subject of your photo to stay in focus and the background out of focus. It all depends on the effect you are trying to achieve. When this happens, it is referred to as shallow depth of field. When on a shallow depth of field, you can easily focus on your subject, but objects closer or further from the subject will not be focused on. When using a DSLR camera, a shallow depth of field can be achieved by choosing a wide aperture such as f/1.4.
When using a small aperture, your photos will have a deep depth of field. Thereby, more of the photo will be in focus. This is ideal when you are taking a landscape photo and need the background and foreground objects to be in focus.
In point-and-shoot cameras, you have no control of the aperture. Therefore, it is difficult for you to achieve a shallow depth of field. If you still need a shallow depth, you can zoom in and concentrate the focus on your subject. DSLR and bridge cameras allow you more control over the depth and field and, thereby, bring out your artistry and creativity to focus. This also gives you control over your photos.
Scene Modes
Scene modes are presets in most cameras. You can access the scene modes from the menu. In some cameras, there is a dial at the top of the camera from where you can choose the scene modes.
Scene modes are geared to a given situation. When you choose SPORTS, the scene mode will use a fast shutter speed and also activate motion detection to reduce blur. You can choose portrait mode to focus on the subject of your photo with ease. The scene mode also allows you to adjust color balance, allowing skin tones to appear natural.
Even when you do not adjust the scene mode of your camera, automatic adjustments and the photo will still appear sharp. In a camera that allows you to select the scene mode, the quality of your photos will be highly enhanced. Therefore, it is advisable to use them as often as possible.
(Canon)
White Balance
When you are taking photos, the intensity of different colors has to be controlled. This typically refers to the primary colors blue, red and green. The reason behind this is to render correctly. Gray balance is the most common method used.
Color balance enhances the look of a photo and can be used for color correction. Color correction comes in handy, seeing that the original image for the sensor of the camera does not match the human eye. Therefore, the camera needs to compensate for the differences.
White balance, on the other hand, is a setting that allows you to create natural coloration in your photos. When the white is balanced right, you will achieve accurate colors. Put simply, the color of the photo you take is affected by the lighting selected. The human eye and the brain will compensate for the light differences. Here, a red object will appear red irrespective of whether it is viewed in fluorescent, incandescent or sun light.
White balance compensate for the differences in light between the eyes and the camera. You can change the lighting of your camera from the white balance settings. This lets you choose between incandescent, fluorescent, daylight, shade, flash or cloudy. You can also set the white balance to adjust automatically.
Metering
Metering refers to the measure of the brightness of your photo subject. Your camera will automatically adjust the shutter speed, aperture and ISO number based on the brightness of your subject. Each camera has a built-in metering sensor.
A sensor does not just measure the brightness of the subject, but that of different parts of the photo frame. There are three methods through which a camera can meter light:
Spot Metering: This is where the camera meters light indicated by a spot. Spot metering is ideal when the subject of your photo is a small spot that needs enough exposure. This gives you the assurance that the spot is well exposed even in dimly lit situations and in situations where the background is too dark or too bright.
Matrix Metering: This is the most common form of metering. Here, the camera frames the entire field and sets exposure for the best image.
Centered Weighted Metering: Here, the camera meter the subject, background, and foreground then assigns value to the area enclosed by a circle. This is ideal when there are varied light conditions within the frame. This kind of metering has been used for a long time for portraits.
You need to choose a metering method based on your artistic needs and the scene.
Understanding Composition And Guidelines To Make Your Photos Much More Interesting
When taking photos, you have to get the settings right for sharpness and clarity. Beyond that, it is up to you to tweak the position of the camera to get a good photo. There are no rules to follow, just guidelines to enhance the appearance of your photos.
There are a number of composition guidelines you can apply in any shooting situation to enhance the impact in different scenes. When used right, these guidelines will allow you to get natural photos, bring better focus on important parts of a scene and even lead the viewer through the images.
Most of the composition guidelines are universal. When you get used to them, they become part of your shooting, and you can apply them even without realizing that you are. Following the composition guidelines makes the difference between taking photos fast and spending a lot of time focusing on a scene.
Below Are Some Of The Composition Guidelines:
Rule Of Thirds
Your photo needs to be balanced. This can be achieved by correctly positioning the most important parts of your photo. You can do this by imagining that your photo frame is divided into a three by three matrix. The photo subject needs to be placed along the lines that divide the frame or at the points of intersection.
Most digital cameras will offer you grids over the LCD screen. This makes it easy for you to place your photo. When an image is placed on the intersection of the grids, the background, foreground and subject are balanced.
When the photo subject is placed off-center, the photo appears more interesting, but it leaves a space on one side, which can result to a feeling of emptiness. Granted, the space needs to be occupied by another object of lesser importance. This brings balance.
Even when you want to focus on an up-close object, you need to have a far object on the other side of the photo to enhance balance.
Leading Lines
When you place lines on your photo, you enhance the way the photo is viewed. This is so because the human eye is drawn towards lines. Lines pull us close to the photo. There are different types of lines that you can use on your photos including diagonal, horizontal, vertical, zigzag, curvy and radial among others.
You can achieve this by capturing roads, electricity lines and any other elements that show lines.
Symmetry And Patterns
In any scene, there is symmetry and patterns either man-made or natural. Symmetry or pattern on a photo adds an artistic touch and enhances your composition. You can break the symmetry or pattern to introduce a focal point or tension on the scene.
Identify A Viewpoint
A viewpoint is a vantage point from where you take your photo. A viewpoint makes the difference between a good photo and a poorly taken photo. When you choose a good viewpoint, you are able to focus on the subject of your photo well and affect the story a photo carries. Besides shooting from eye level, you can shoot from high above, from the side, back, or ground level.
Background
When the background acts as the sensation of your photo, you will not have a good shot. The human eye distinguishes between different elements in a scene, but the camera cannot. However, it is possible to overcome the problem when you are shooting. You need to look for a plain background, less busy.
A good photo background should not distract the eye from the photo subject.
Depth
When composing, you need to create a good depth with the elements on the photo. This allows the eye to tell the actual depth on the scene. This is easily done by including objects on the foreground, middle and background. You can also overlap the elements by obscuring one object with another.
When you create depth, our eyes will distinguish between the layers, allowing the subject of the image to be the sensation. You can add interesting objects on different distances from the camera.
Framing
When you add a frame on the edges of your photos, you are able to isolate the subject from the other parts of your photo. There are lots of natural frames you can use including trees, holes and archways. Successful addition of frames result to a more focused image and draws your eye to the point of interest.
Hills have been used for a long time to create focal points.
Cropping
When the subject of your photo is so small, it gets lost in the details of the clustered surroundings. You can crop the subject tight, eliminating a busy or noisy background, making the subject of your photo the sensation.
Cropping is simply cutting out the excess details. Digital photography has made it easy for you to experiment with different composition techniques without worrying about film costs and you never run out of shots. You can shoot different shots, choose the best and delete the rest. And there are no extra costs.
When you are experimenting, different concepts will work and others will not work. You can focus on lines, frames and other subjects within a photo and have as many shots as possible.
Common Mistakes Every Beginner Will Make
You might be so excited when you buy your first DSLR camera, but it only takes a few days and your excitement wears out because you cannot get the shots you dreaded for. You know an SLR camera is supposed to give you quality photos, but that is not happening. Why? Because you are making one or more mistakes common with beginner photographers.
As a beginner, it does not matter whether you spent hundreds of hours in college or at home reading about photography, you still get frustrated. Sometimes, it is not that you do not know the guidelines, but you might be forgetting a thing or two. Below are some of the common mistakes made by beginners.
1. Wrong White Balance
While the eye can distinguish between different colors, the camera does not. It is, therefore, up to you to choose a good white balance to ensure that the different colors are well balanced.
When shooting on a bright sunny day, then you set the white balance to cloudy, an orange cast will be seen, and on a cloudy day when the white balance is set to daylight, a blue cast is seen.
If you do not know how to set the white balance, set it to adjust automatically.
2. Unbalanced Brightness
While your eyes can distinguish between the different elements even when the brightness varies, the camera cannot. This is because the dynamic range of the camera is different from that of your eyes. Put simply, dynamic range is the ratio between the darkest and brightest elements in a scene.
As a photographer, you need to enhance the exposure of the different elements in your photo to enhance the outcome. To the human eye, overexposed patches on the photo are more unacceptable than underexposed patches.
When using a DSLR camera, it will give you highlight warnings, showing you regions that are overexposed during image playback. When the blinking extends, make exposure compensation.
3. Placing The Subject In The Center
When the subject of a photo appears in the center, it creates a boring and artistically unappealing photo. Here, there is nothing else to look at for the viewer. Granted, you need to apply the rule of thirds to create an appealing photo. However, remember not to leave an empty space.
4. Wrong Focus
When the focus is not right, you will have blurred photos. The main focus of your photo needs to be in sharp focus. If this does not happen, the viewer will be distracted and lack interest on the photo.
Because the eye sees clear images, we expect them to appear clear and sharp on a photo. You need to check the focus by zooming in on your subject to ensure there is enough light and color contrast. You can use autofocus when manual focus cannot work.
5. Busy Background
A background will ruin photos. It is one of the most common mistake with beginners. You concentrate so much on the subject of the photo and end up forgetting the background.
There is nothing wrong with giving the background some attention, but this ends up ruining the shot as the viewer might concentrate on something else and forget the subject. When shooting, start by identifying the subject. Forget the subject and concentrate on other aspects of the scene to find things that will complement your subject.
6. Crooked Horizon
The horizontal contributes to the balance in a photo. The first thing a viewer will see is a skewed horizon. But a lot of photos have crooked horizons, which make subjects appear like they are falling. When you ware composing your photo, you can use the grid overlay to frame the photo.
7. Photos With No Depth
When there is no depth, the viewer cannot tell the distance between two elements in a photo. Seeing that photos are two-dimensional, focusing on the foreground, middle and background and elements allow you to create depth. When this does not happen, the resulting photo is a disappointment.
8. Cluttered Photo
When you want to capture a lot in a single photo, you end up with a photo that looks confused. This happens when you look at a scene as a single unit. Instead of taking a photo with so much detail, choose a single element that interests you and put emphasis on it.
You can try different compositions to accommodate as much detail without creating a cluttered appearance.
9. Bad Light
Light is key in photography. With no light at all, there is no photography. Light has different qualities and direction. You will have great shots in the golden hours; a few hours before sunrise and a few hours before sunset.
When the light is too harsh or is too dim, the photo will appear low quality. When you learn to focus on the light, you become a better photographer.
Conclusion
Photography should be fun and interesting. But only when you learn the basics of photography. There are different cameras to choose from when you are getting started. A good SLR camera will not cost you much and will offer you great quality photos. Your budget will limit your camera choices.
When buying a camera, consider the aperture, the resolution and the features of the camera. Some cameras allow you mode manual settings than others. Which is a good thing as you have enough control of the photos you take. Additional features such as built-in flash let you take photos in different situations.
Input and output terminals make it easy for you to access your photos from a computer. You can also consider the accessories that come with your camera including carrying straps, lenses, memory cards, USB cables, batteries and tripod. These make it easy to get started.
When shooting, remember that the only rules that exist are those you create. You can, therefore, shoot in any way that you want as long as you follow the simple guidelines above.



